“Write the paper as though no editor will ever see it … then let a good editor make sure everyone does.” — Anonymous Peer‑Reviewer
Introduction
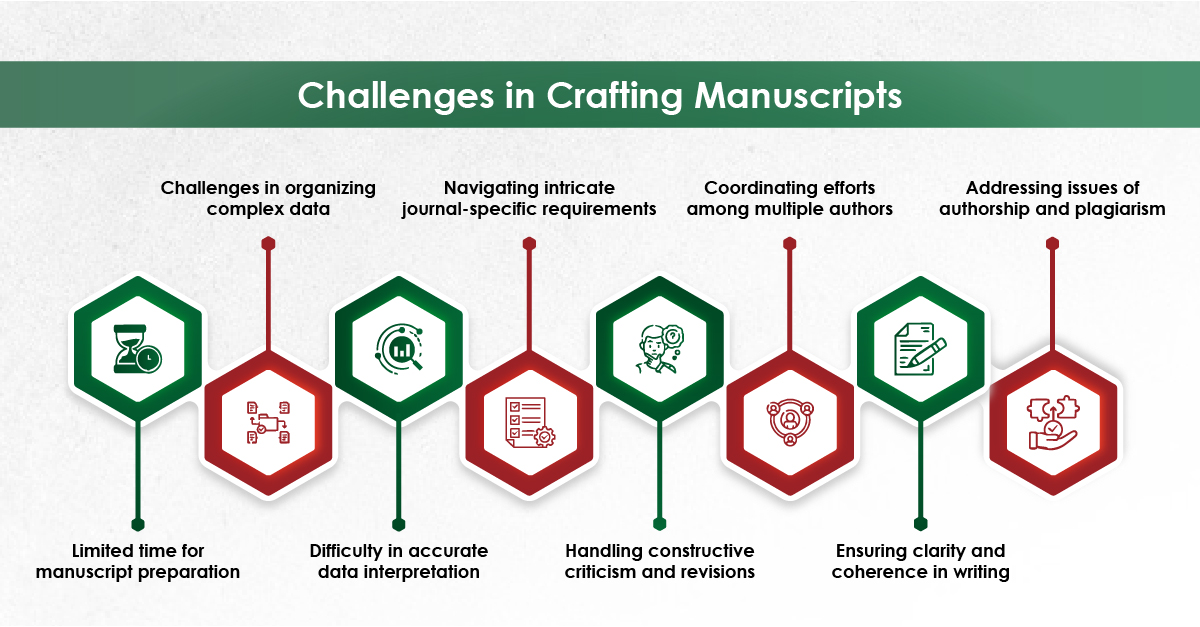
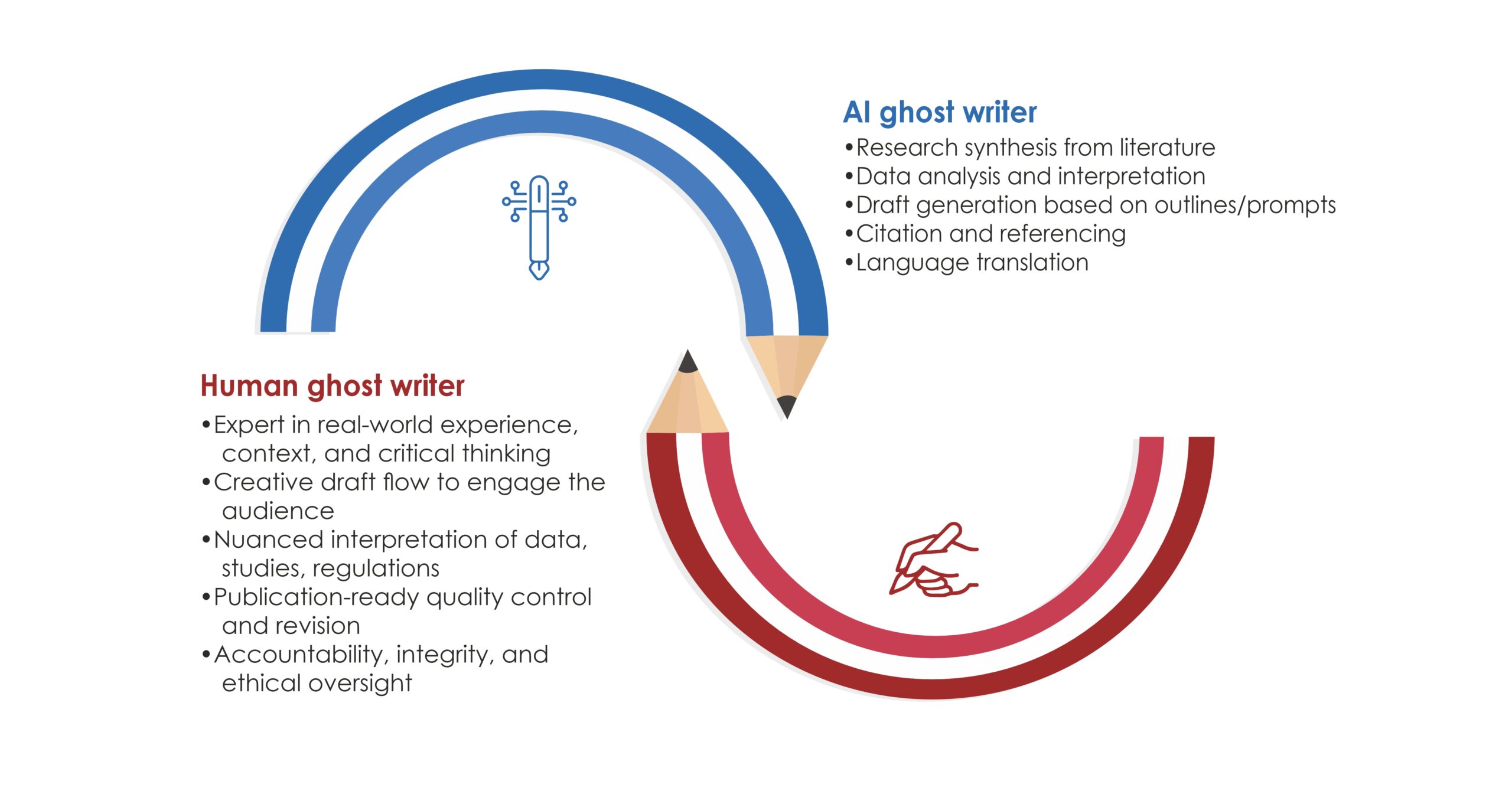
In the era of hyper‑competitive research, scholars juggle with laboratory work, teaching loads, clinical duties, and an ever‑growing expectation to publish quickly. This demanding environment requires well-structured, clear writing with proper grammar and language quality. In the health‐sciences journals, a surveyed by Johnson & Miller (2023) reported that approximately one‑fifth of manuscript received first round rejections due to poor language quality.¹ As a result, many researchers turn to academic research writing services for professional support.
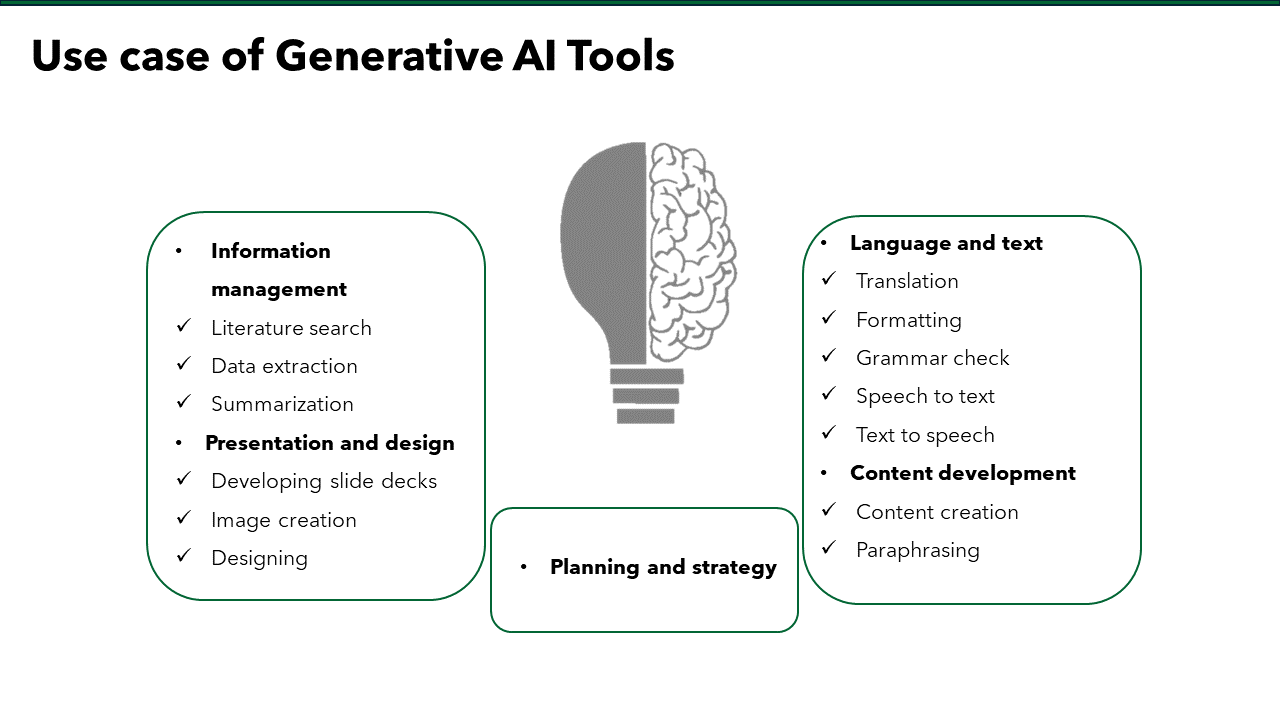
These services can amplify your productivity when it used transparently and within institutional policies, without compromising authorship or academic integrity. Below we outline seven evidence‑backed benefits, the ethical safeguards you must observe, and practical tips for choosing the right provider.
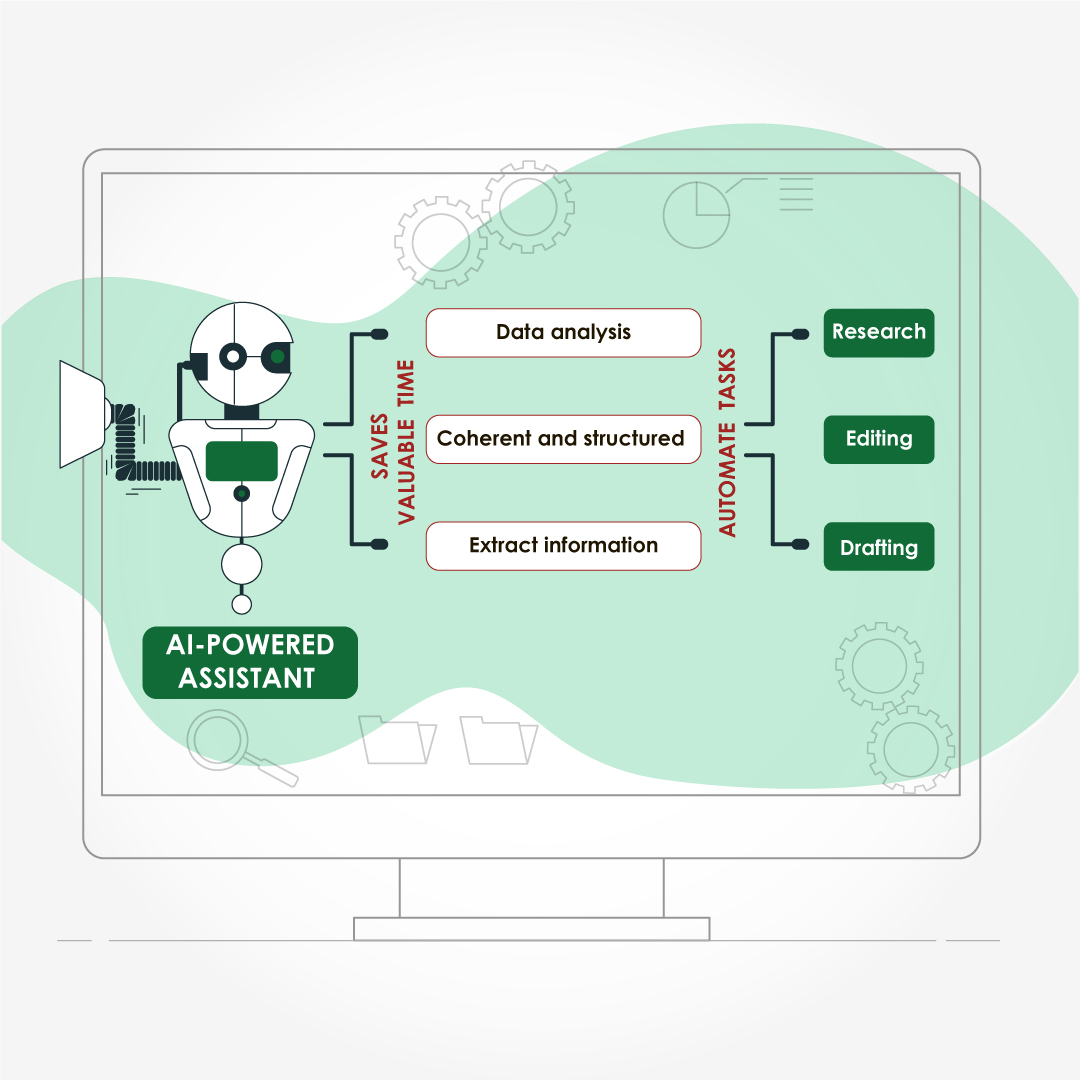
- Save Time and Lower Stress
- Drafting & structural editing free up hours during grant‑cycle crunches
- Formatting & reference management eliminate repetitive tasks
A R01 applicant survey showed that outsourcing technical editing saved principal investigators a median of 7.5 hours per submission.²
- Access Field‑Specific Expertise
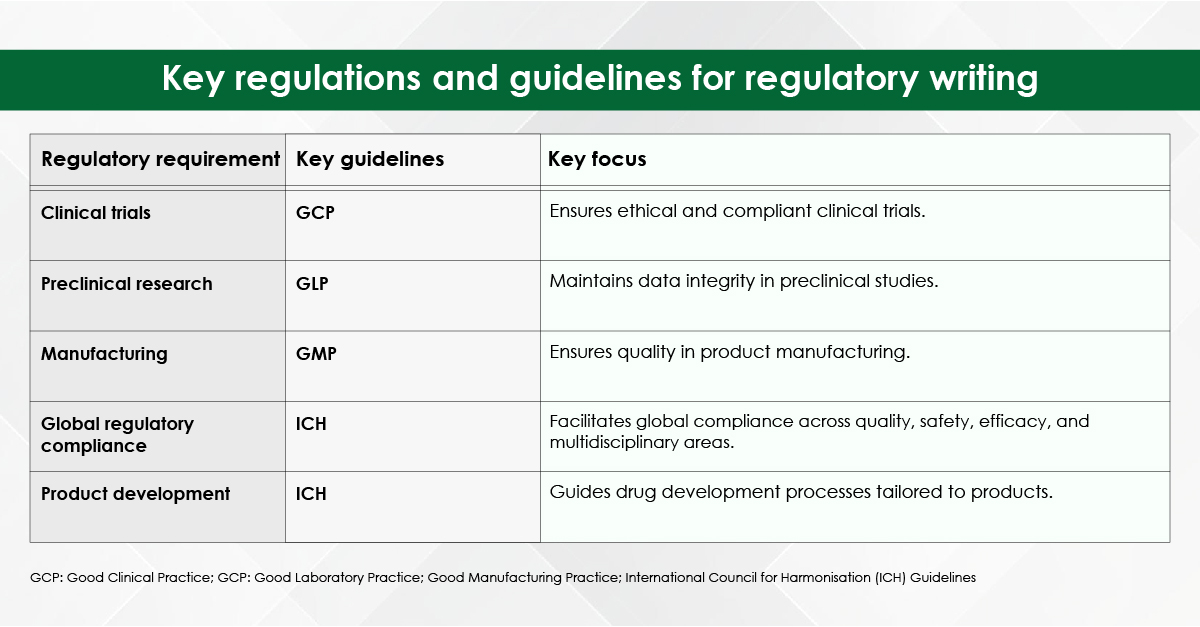
Reputable agencies recruit writers with advanced degrees (often PhDs or PharmDs) in specialties ranging from bioinformatics to nurse education. Their familiarity with discipline‑specific terminology, preferred reporting guidelines (e.g., PRISMA, CONSORT), and target‑journal scope improves the likelihood of favourable peer review.
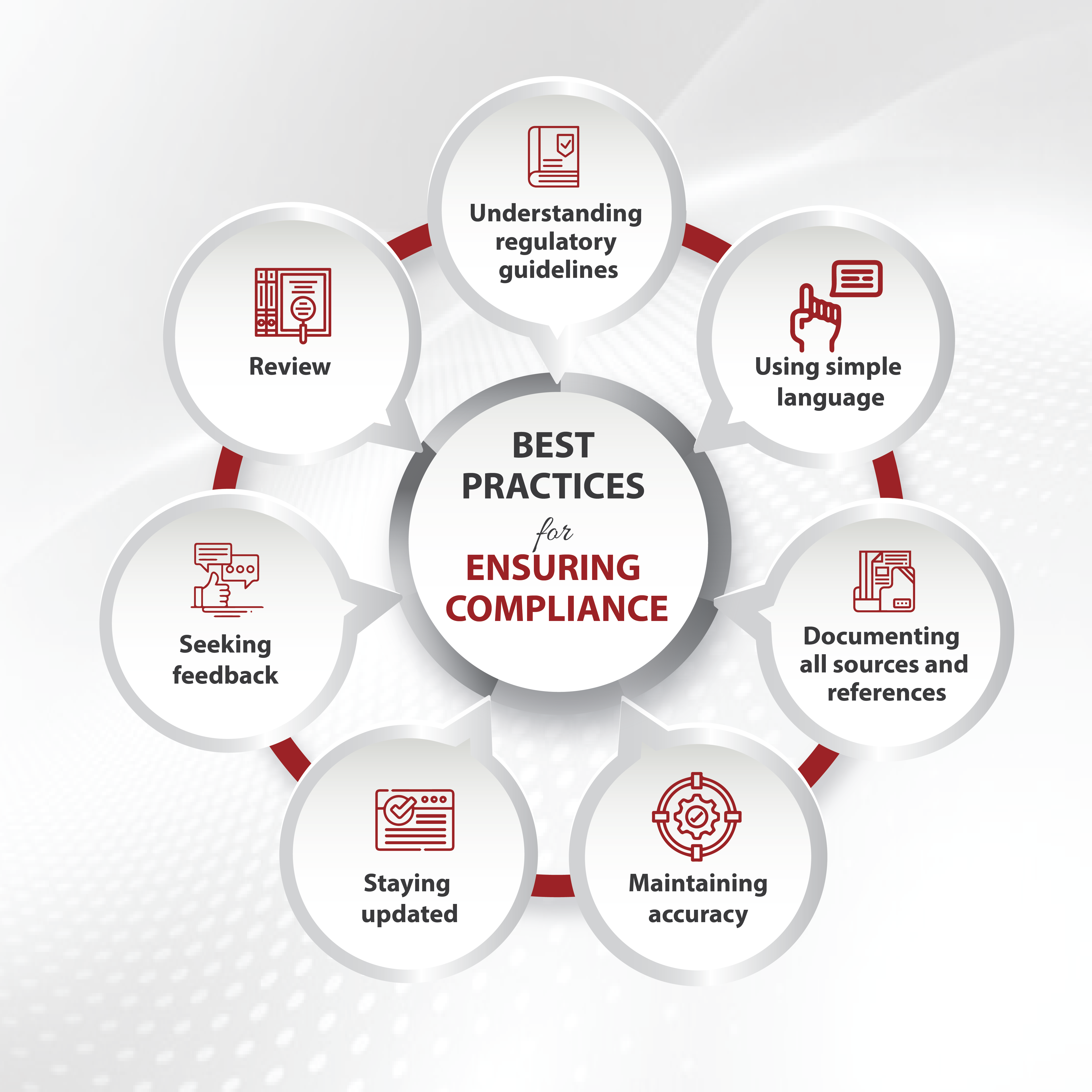
- Ensure Technical & Regulatory Compliance
Professional editors keep abreast of style manuals (Vancouver, APA, AMA) and evolving journal requirements such as data‑sharing statements and graphical abstracts. A compliant manuscript avoids immediate desk rejection for formatting errors.
- Robust Plagiarism & Similarity Screening
Premium services run every draft through similarity‑detection suites (iThenticate, Turnitin) before you upload to the journal portal. You receive a similarity report along with guidance on legitimate paraphrasing and quotation.
- Comprehensive Research Support
Beyond writing, many firms offer:
- Systematic literature searches (with librarian peer review)
- Statistical analysis plans
- Data‑visualisation assets
- Response‑to‑reviewers letters
This end‑to‑end model streamlines the entire publication life‑cycle.
- Tailored Deliverables for Every Project
Whether you require a 300‑word conference abstract, an NIH R21 grant, or a 40‑page scoping review, services can scale and customise outputs to your word count, rubric, and journal guidelines.
- Collaborative Skill Development
Annotated edits, tracked‑changes files, and explanatory margin comments turn each project into a master‑class in academic writing. Over time, clients report noticeably clearer prose even when drafting solo.
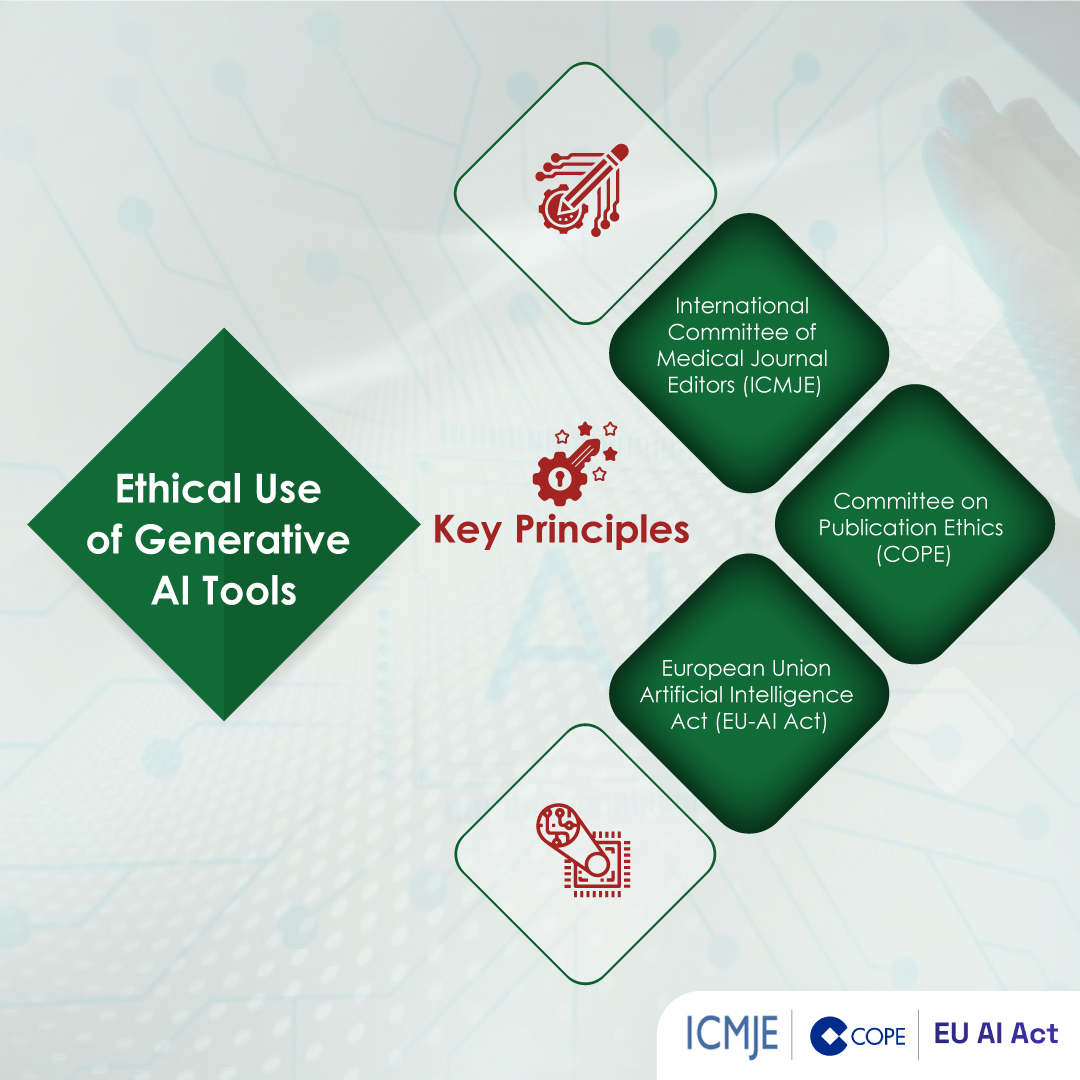
Balanced Considerations & Ethical Safeguards
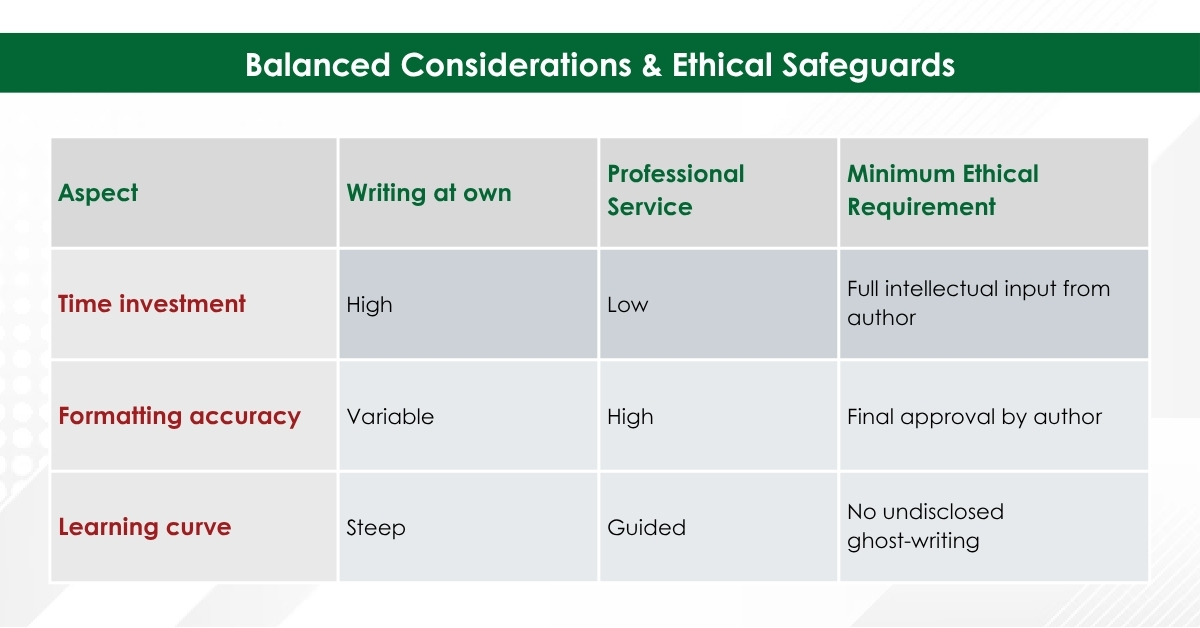
- Authorship Responsibility: Per ICMJE and COPE, authors must retain ownership of ideas, data, and final wording. Writing support does not equal authorship unless substantive intellectual contribution is added.
- Institutional Policies: Always confirm your university or funder permits external editorial services.
- Disclosure Statement: Good practice includes a note such as:
“Editorial assistance was provided by XYZ Medical Communications in accordance with journal policy; all authors approved the final manuscript.”
Final Thoughts
Academic research writing services, when used responsibly, can transform overwhelming writing tasks into efficient, high‑quality outputs—freeing you to focus on discovery, patient care, and teaching.
At Turacoz, we offer comprehensive Academic Research Writing Services designed to bridge the gap between brilliant research and compelling communication. Our commitment extends beyond mere editing—we partner with researchers to enhance clarity, ensure methodological rigor in presentation, and maintain the highest standards of academic integrity. Whether you’re navigating your first publication or seeking to accelerate your research output, our expert team stands ready to help transform your valuable insights into impactful, publication-ready manuscripts that advance both your career and your field of study.
References
- Johnson R, Miller C. Common reasons for manuscript rejection: an analysis of peer‑reviewers’ comments. J Schol Publishing. 2023;54(1):45‑56.
- Smith A, Gupta P. Time savings associated with professional editorial support during NIH grant preparation. Res Manage Review. 2022;37(2):125‑131.



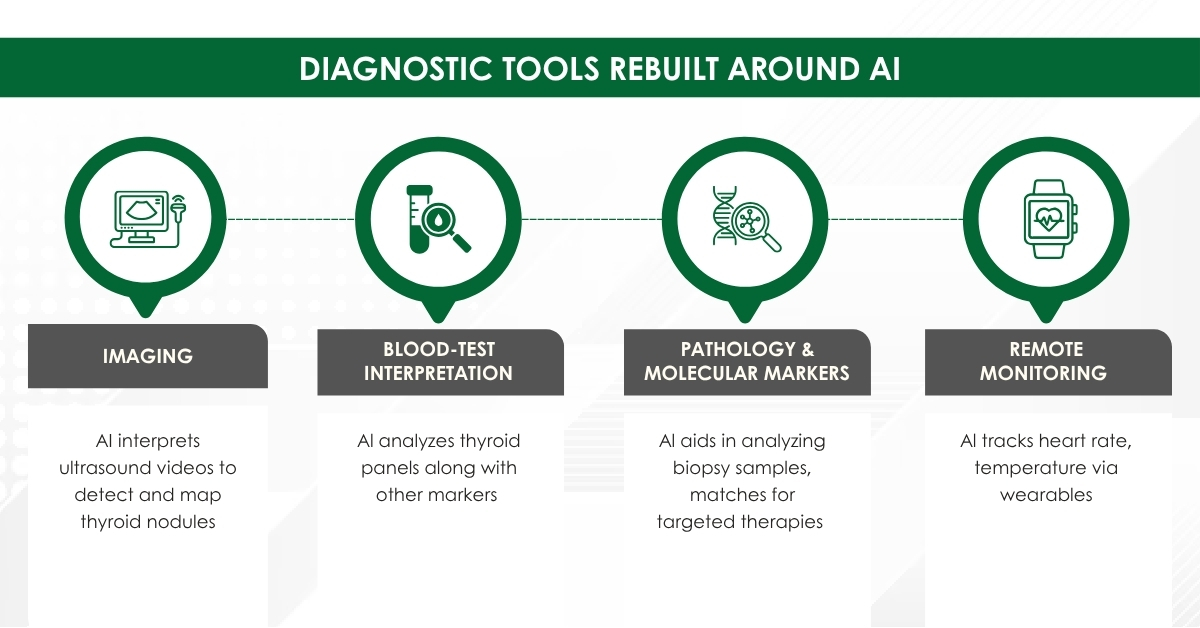


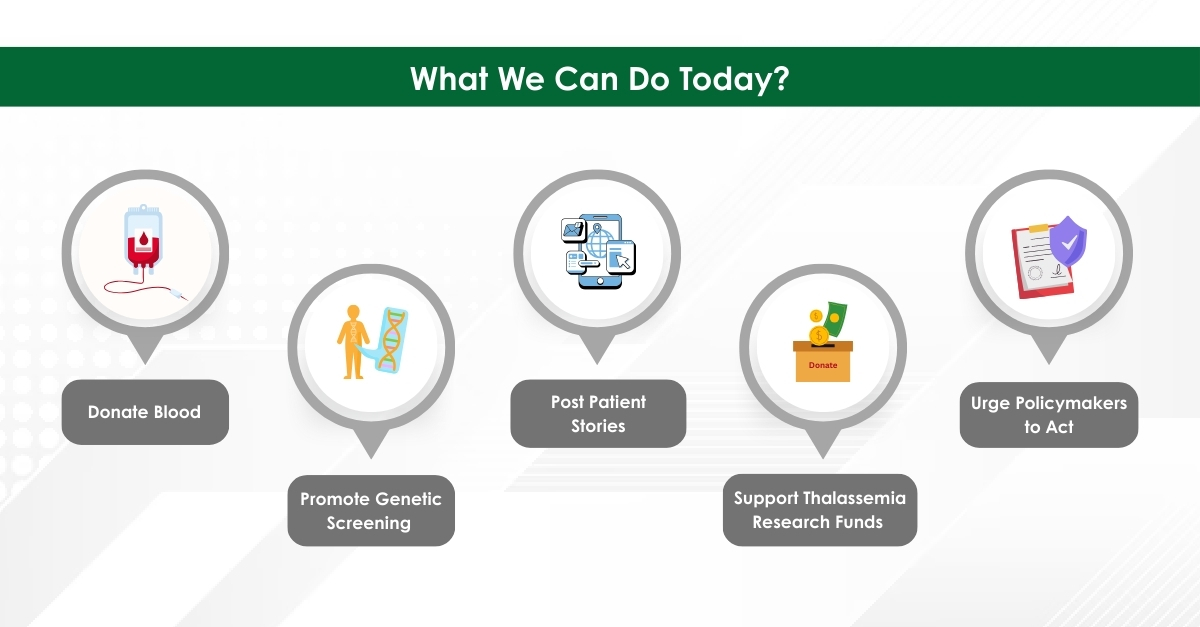




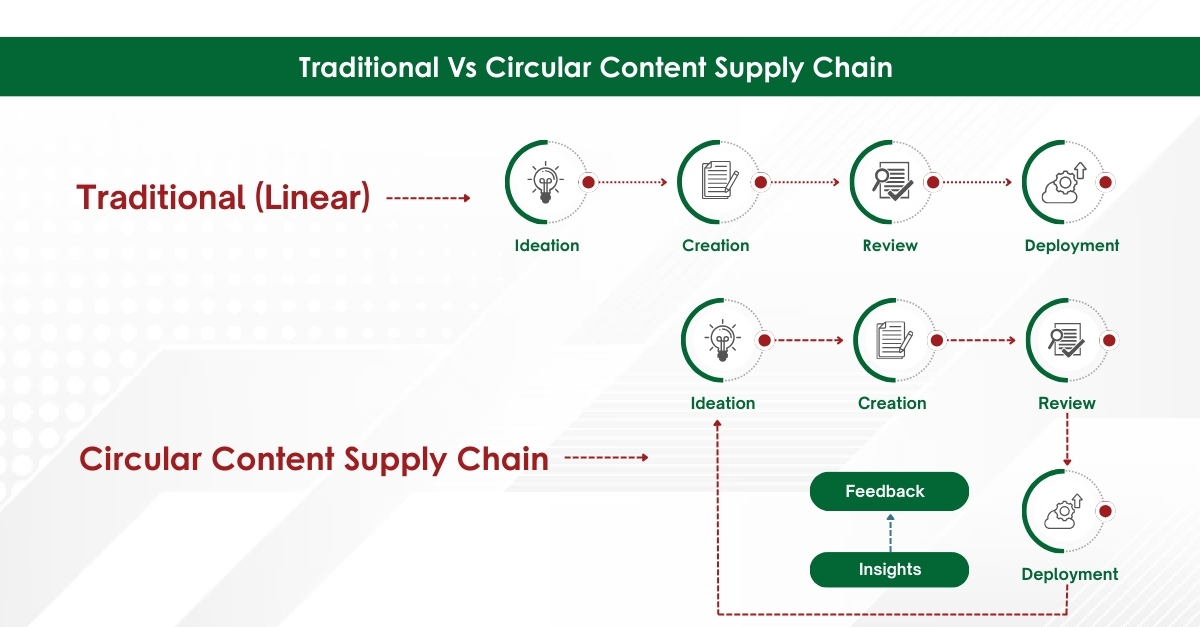









































































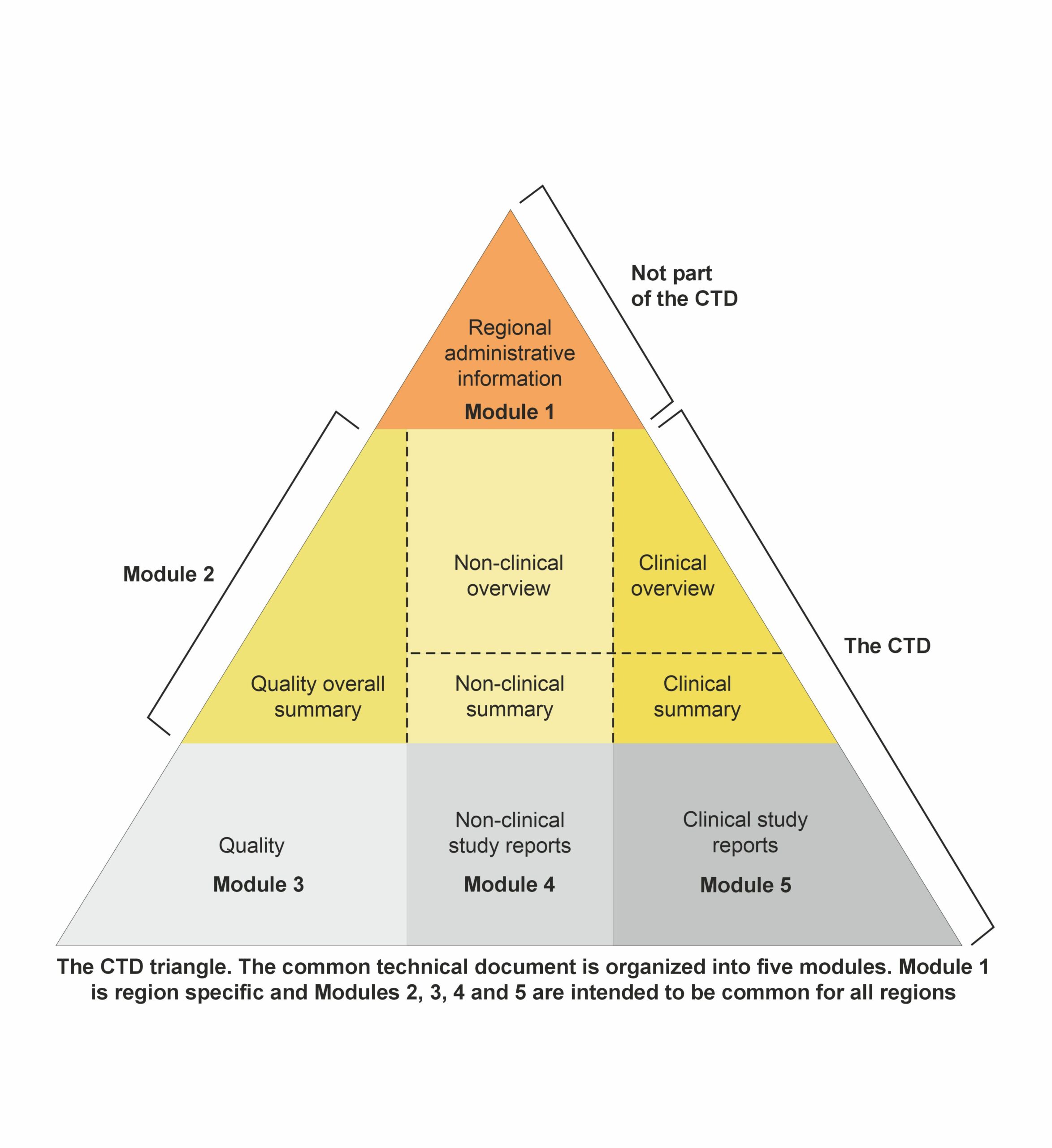 Module 1: Administrative and prescribing information
Module 1: Administrative and prescribing information