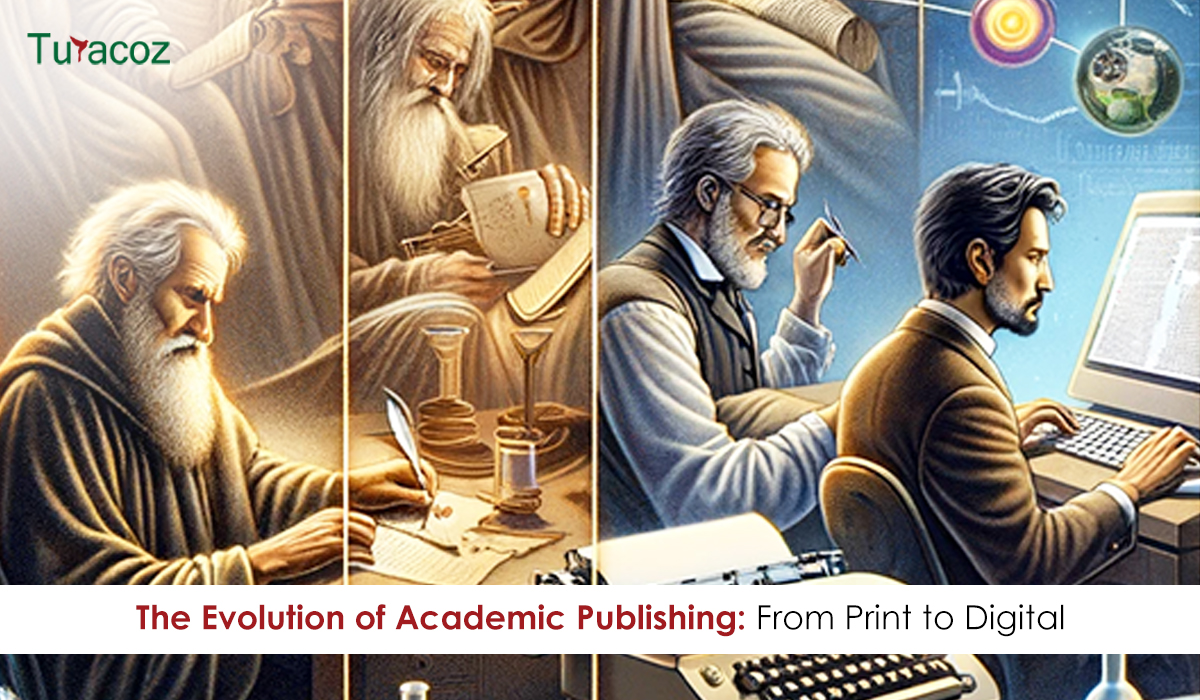
For centuries, the world of academic publishing was dominated by the printed word. Scholarly journals, monographs, and textbooks were carefully typeset, printed on paper, and distributed through a network of publishers, libraries, and bookstores. However, the rise of the Internet and digital technologies has ushered in a seismic shift in the creation, sharing, and preservation of academic knowledge. The transition from traditional print to digital formats has brought significant changes and opportunities for scholarly publishing.
- Traditional Print Era
- Historical Context
The origins of academic publishing were traced back to the 17th century, with the establishment of some of the first scientific journals, such as “Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society” in 1665. For centuries, the print media has been the primary vehicle for the dissemination of scholarly work. Journals, often affiliated with academic societies, were revered to be the cornerstone of academic communication.
- The Role of Print Journals
Print journals play a crucial role in shaping the field of academics:
- Validation and Peer Review: Print journals establish a rigorous peer-review process, ensuring the credibility and quality of published research.
- Archival Value: Physical copies of journals provided a tangible archival record that future scholars could access and reference.
- Limited Accessibility: Access to print journals was often restricted to those affiliated with institutions that could afford costly subscriptions, limiting the reach of academic knowledge.
2. Digital Revolution
Emergence of Digital Formats
The seeds of the digital revolution in academic publishing were planted in the late 20th century with the advent of electronic databases and online repositories. Initiatives such as JSTOR and Elsevier’s ScienceDirect have begun digitizing academic journals, making them accessible to researchers and students through institutional subscriptions. This initial foray into digital publishing provided a glimpse into the potential for wider dissemination of scholarly work and more efficient information retrieval.
As the Internet became more ubiquitous and bandwidth increased, publishers started experimenting with online journals and e-books. These early digital formats offered several advantages over their print counterparts, including lower production and distribution costs, faster publication cycles, and the ability to incorporate multimedia elements.
Benefits of Digital Publishing
The shift to digital formats brought a plethora of benefits:
- Accessibility and Reach: Digital publishing democratized access to academic research. Scholars, students, and practitioners worldwide can access journals without geographic and financial constraints of print subscriptions.
- Speed and Efficiency: The digital medium significantly reduced the time lag between submission, peer review, and publication. This accelerated the dissemination of new findings and fostered timely academic dialogue.
- Interactivity and Multimedia: Digital platforms allowed the inclusion of interactive elements, such as hyperlinks, videos, and datasets, enhancing the depth and engagement of scholarly articles.
- Searchability and Discoverability: Advanced search functions and indexing made it easier for researchers to find relevant literature, boosting the visibility and impact of published work.
- Environmental Impact: Reducing the need for physical copies helped decrease the environmental footprint of academic publishing.
3. Open Access Movement
One of the most significant developments in the digital era of academic publishing is the emergence of the open access (OA) movement. Driven by the belief that scholarly research should be freely available, OA initiatives aim to remove barriers in accessing and sharing academic content.
OA publishing models typically fall into two categories: gold open access, where authors or their institutions pay article processing charges to make their work openly available immediately upon publication, and green open access, where authors self-archive their works in institutional or subject-specific repositories after an embargo period.
Prominent OA publishers like the Public Library of Science (PLOS) and BioMed Central have played a pivotal role in advancing open access, while traditional publishers have also adopted hybrid models that allow authors to make their articles open access upon payment of a fee.
Benefits of Open Access
- Increased Visibility: OA publications are more widely read and cited, which increases the impact of research.
- Equity: OA ensures that researchers from underfunded institutions and developing countries can access the latest findings and foster global academic collaboration.
- Public Engagement: By making research freely available, OA bridges the gap between academia and the public, promoting informed societal discourse.
Challenges in the Digital Era
Despite its numerous benefits, the transition to digital publishing has presented several challenges:
- Quality Control and Predatory Journals: The ease of digital publishing has led to the proliferation of academic journals, including predatory journals that exploit the OA model. These journals often lack rigorous peer review and publish substandard research for profit, undermining the credibility of academic publishing.
- Financial Sustainability: The traditional subscription model provided a steady revenue stream for publishers. While democratizing access, the OA model raises questions about financial sustainability. Many OA journals rely on article processing charges (APCs) paid by authors, which can be a barrier for researchers without sufficient funding.
- Technological Barriers: While digital platforms have enhanced accessibility, they also require a robust technological infrastructure. Researchers in regions with limited Internet access or digital literacy may still face barriers in accessing and publishing research.
- Data Security and Privacy: The digital environment pose risks related to data security and privacy. Ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of scholarly work in an online setting is paramount, requiring continuous advancements in cybersecurity measures.
- Intellectual Property Concerns: The shift to digital formats has sparked debates over intellectual property rights. Balancing the open dissemination of knowledge with the protection of authors’ rights and preventing unauthorized use or distribution of content remains a complex issue.
4. Future of Academic Publishing
Integration of Advanced Technologies
The future of academic publishing is poised to integrate advanced technologies and to further enhance the research ecosystem:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can streamline the peer-review process, detect plagiarism, and assist in identifying relevant literature, making the publication process more efficient and robust.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain can provide secure and transparent records of publication histories, ensuring the integrity and traceability of scholarly work.
- Data-Driven Insights: Big data analytics can provide valuable insights into research trends, impact metrics, and collaboration networks, informing strategic decisions in academic publishing.
5. Enhanced Collaboration and Interdisciplinary Research
Digital platforms facilitate collaboration across geographical and disciplinary boundaries. The future of academic publishing will likely see increased interdisciplinary research, addressing complex global challenges through a holistic approach.
6. Continued Advocacy for Open Access
The push for OA is expected to intensify, driven by advocacy from academic communities, funding agencies, and policymakers. Sustainable OA models that balance accessibility with financial viability are crucial in shaping the future of academic publishing.
The evolution of academic publishing from print to digital has transformed the dissemination and accessibility of scholarly research. While the digital revolution has brought significant benefits, it has also introduced new challenges that require ongoing adaptation and innovation. As technology continues to advance, the academic community must navigate these changes thoughtfully, ensuring that the pursuit of knowledge remains inclusive, credible, and impactful. The future of academic publishing holds immense potential, promising to further democratize access to knowledge and foster a vibrant, interconnected global research community.
At Turacoz Healthcare Solutions, we understand the evolving landscape of academic publishing and are committed to supporting scholars in navigating these changes. Beyond our expertise in journal publication, we offer a comprehensive range of academic services designed to enhance the quality and impact of scholarly work. Our services include book writing, thesis writing, authoring book chapters, and providing tailored support to meet the diverse needs of the researchers. Whether you are crafting a detailed monograph, developing a critical thesis, or contributing to collaborative volumes, Turacoz Healthcare Solutions is your partner with academic excellence. Reach out to us at www.turacoz.com to ensure that your work achieves its full potential in the digital age.